CATEGORY > Customer Success Management
Customer Success Automation: From Manual Magic to Scalable Strategies in B2B SaaS

Introduction
Feeling overwhelmed by all the repetitive tasks on your customer success plate?
Wouldn't it be great to free up some time to focus on what really matters – building strong relationships and helping your customers achieve their goals?
That's where customer success automation comes in!
Think of it as your super-powered sidekick, handling mundane tasks like onboarding emails, scheduling meetings, and even sending out automated support resources.
This lets you, the customer success superhero, focus on the strategic stuff – personalized outreach, in-depth consultations, and becoming a trusted advisor to your customers.
Imagine being able to spend more time crafting winning customer success plays or diving deep into customer data to identify potential roadblocks.
Automation empowers you to do just that, by streamlining processes and giving you back valuable time.
Let's chat about how customer success automation can help you take your customer success game to the next level!
In this guide, we explore the need, challenges, and automation possibility for 3 critical areas: Onboarding, engagement, and retention
1. Pre-Automation Onboarding
New customers were welcomed with a flurry of emails, phone calls, and personalized training sessions – a time-consuming but essential step in establishing a positive first impression.
Before customer success automation streamlined onboarding experiences in B2B SaaS, the process relied heavily on manual efforts.
While these methods fostered strong relationships, they lacked scalability and struggled to keep pace with growing customer bases.
Let's delve deeper into the world of pre-automation onboarding and explore the challenges it presents:
I. Personalized Greetings
Customer success managers (CSMs) shouldered the responsibility of crafting personalized welcome emails for each new customer. This ensured a warm introduction and set the tone for the relationship, but it became increasingly time-consuming as companies scaled.
II. Knowledge Dissemination
New customers were bombarded with information during onboarding calls or in-person sessions.
These sessions, while valuable, were resource-intensive and limited the scalability of the onboarding process.
Standardized training materials like user manuals or basic tutorials often weren't readily available or lacked the level of customization needed for specific customer needs.
III. Feature Exploration
CSMs would often guide new customers through the product's core functionalities, providing live demonstrations and hands-on training. This personalized approach ensured a strong understanding of the product, but it limited the number of customers a single CSM could effectively onboard.
IV. Post-Onboarding Support
Following the initial onboarding session, customers often relied on email or phone calls for ongoing support. This reactive approach meant issues might not be addressed promptly, potentially leading to frustration and hindering customer adoption.
The Challenges Of Manual Onboarding
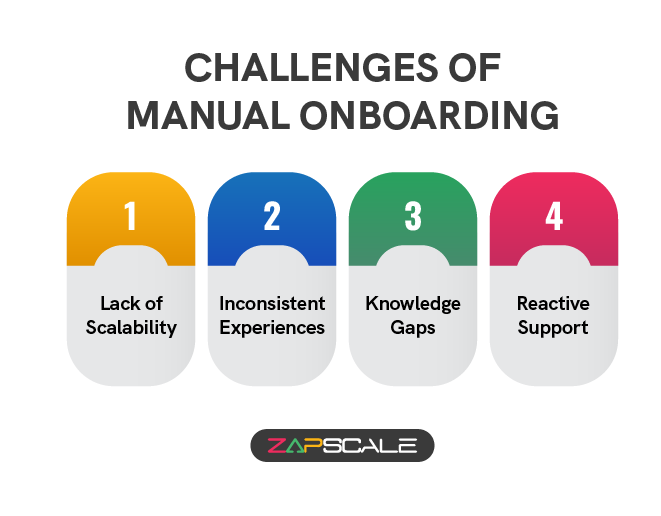
I. Lack Of Scalability
As the customer base grew, the manual approach to onboarding became unsustainable. CSMs simply didn't have the time to personalize onboarding experiences for hundreds or even thousands of new customers.
II. Inconsistent Experiences
Reliance on individual CSMs for onboarding led to inconsistencies in the information delivered and the overall experience. New customers might receive different levels of detail or variations in the training approach.
III. Knowledge Gaps
With limited resources for creating and maintaining comprehensive knowledge bases, it was harder to ensure new customers had access to the information they needed, at the time they needed it, to navigate the product independently.
IV. Reactive Support
Waiting for customers to reach out for help after encountering roadblocks meant issues could linger, potentially leading to frustration and hindering their initial product experience.
How Automation Can Improve Customer Onboarding?
While human interaction remains crucial, automating specific tasks within the onboarding process can streamline the experience, improve efficiency, and empower your customers to hit the ground running.
Here are some key areas customer success teams can automate for smoother onboarding:
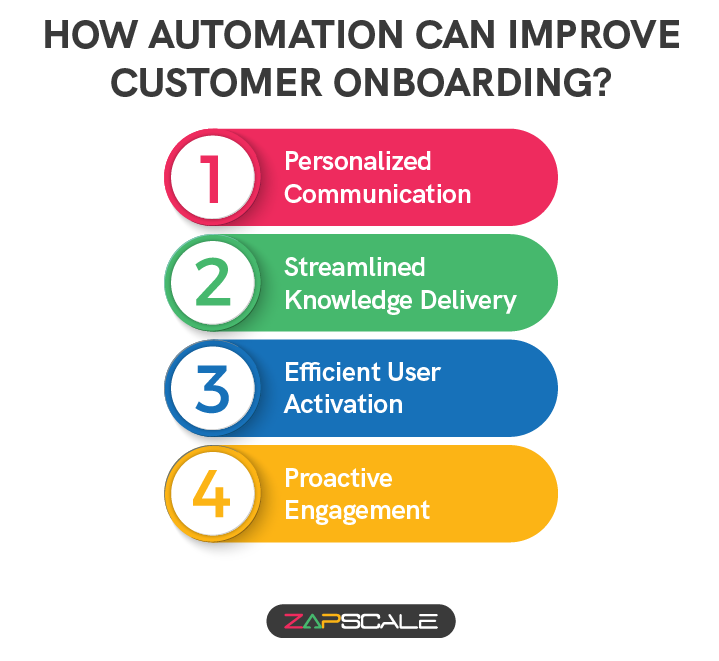
I. Personalized Communication
a. Automated Welcome Emails
Craft personalized welcome email sequences that trigger based on customer signup details. These emails can introduce key contacts, outline initial steps, and provide links to relevant resources.
b. Dynamic Content Delivery
Tailor onboarding content based on customer information like industry, company size, or chosen plan. This ensures they receive the most relevant information specific to their needs.
c. Automated Progress Tracking
Send automated emails or in-app notifications to keep customers informed about their onboarding progress and highlight upcoming milestones.
II. Streamlined Knowledge Delivery
a. Automated Knowledge Base Updates
Utilize automation tools to streamline the creation and maintenance of your knowledge base. This ensures customers have access to the latest information and reduces the burden on CSMs for manual updates.
b. Contextual Help Overlays
Implement in-app contextual help that appears when users hover over specific features or encounter a potential roadblock. This provides immediate and relevant guidance within the product itself.
c. Automated Resource Recommendations
Leverage automation to suggest relevant knowledge base articles, tutorials, or FAQs based on user activity or encountered issues.
III. Efficient User Activation
a. Automated Product Tours
Create interactive product tours that guide users through core functionalities and highlight key features. These tours can be personalized or triggered based on user actions within the product.
b. Automated Task Checklists
Provide automated checklists that outline essential tasks for new users to complete during onboarding. This helps them stay on track and ensure they've covered all the necessary steps to get started.
c. Automated Data Migration ( If Applicable)
For B2B SaaS solutions involving data import, automate the migration process whenever possible. This reduces the burden on both customers and CSMs and ensures a smooth transition from their existing system.
IV. Proactive Engagement
a. Automated Health Score Monitoring
Utilize automated customer health score monitoring to identify potential issues early on. Trigger proactive outreach based on dips in engagement or usage patterns to address concerns before they escalate.

b. Automated Feedback Requests
Send automated feedback requests at key points during onboarding.
This allows you to gather real-time insights into the customer experience and identify areas for improvement.
c. Automated Milestone Congratulations
Celebrate customer milestones with automated messages that acknowledge their progress and encourage continued engagement.
2. Pre-Automation Engagement
Customer success managers juggled calendars filled with check-in calls, product usage monitoring, and ad-hoc support requests.
This reactive approach limited proactive engagement and the ability to identify potential issues before they escalated.
In the pre-automation era of B2B SaaS customer success, keeping customers engaged and maximizing their value relied heavily on manual efforts by customer success managers.
While these dedicated professionals built strong relationships, managing engagement for a growing customer base became a complex juggling act.
Here's a closer look at the manual methods used for customer engagement and their limitations:
I. Calendar Chaos
CSMs' schedules were filled with check-in calls. These personalized calls aimed to assess customer satisfaction, identify potential issues, and ensure users were getting the most out of the product. However, scheduling these calls and ensuring they addressed each customer's specific needs was time-consuming and limited the number of customers a CSM could effectively engage with.
II. Reactive Support
Customer support relied heavily on reactive measures.
Customers would reach out via email, phone, or support tickets when they encountered problems or had questions. While CSMs addressed these issues promptly, this reactive approach meant potential roadblocks might go unnoticed until a customer voiced their concerns.
III. Limited Proactive Outreach
Proactive outreach, a cornerstone of successful customer engagement, was challenging to implement on a large scale. CSMs might identify patterns or potential issues within specific customer segments, but reaching out to each customer individually with targeted advice or resources was resource-intensive and difficult to maintain.
IV. Manual Data Analysis
Understanding customer usage patterns and identifying at-risk customers for proactive intervention relied on manual data analysis. CSMs would sift through reports and usage logs, which was time-consuming and potentially prone to human error.
The Challenges Of Manual Engagement
I. Scalability Issues
As the customer base grew, the manual approach to customer engagement became unsustainable. CSMs simply didn't have the time to conduct regular check-in calls, monitor all customer activity individually, and proactively engage with every customer.
II. Reactive Approach
Relying solely on customers to report issues meant potential roadblocks or areas where they needed additional support might go unnoticed until it impacted their experience or use of the product.
III. Limited Insights
Manual data analysis limited the ability to identify trends, patterns, and at-risk customers on a larger scale. This made it difficult to tailor engagement strategies to specific customer segments or proactively address potential churn.
IV. Inconsistent Interactions
With limited resources and a focus on individual interactions, the level of engagement could vary across the customer base. Some customers might receive more frequent check-ins or targeted outreach than others.
How Automation Can Improve Customer Engagement?
Customer engagement is the lifeblood of long-term success.
Here's what customer success teams can automate for more effective customer engagement:
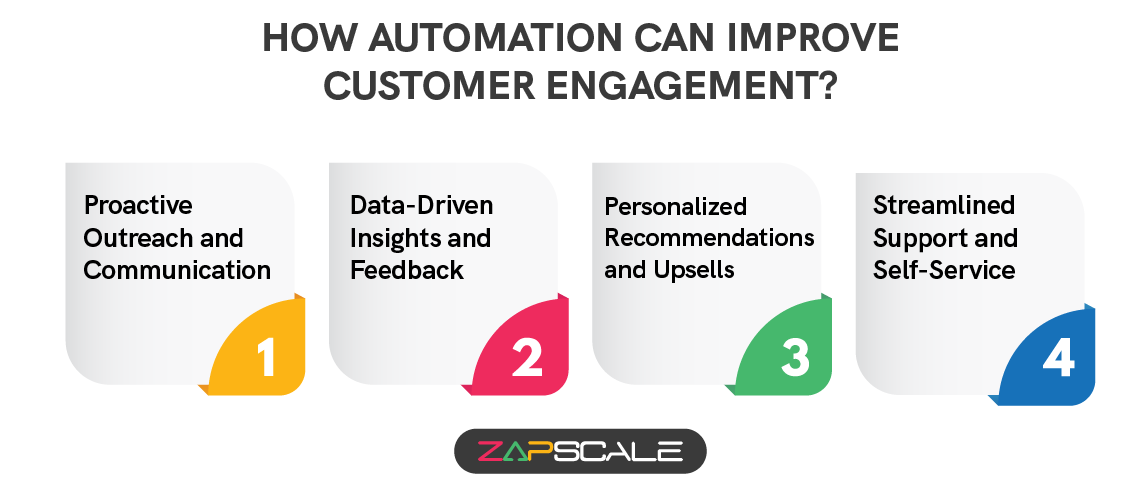
I. Proactive Outreach and Communication
a. Automated Check-in Emails
Schedule personalized check-in emails based on customer segments, time since the last interaction, or product usage patterns. These emails can offer support, highlight new features, or address potential roadblocks.
b. Automated Usage Triggered Communication
Trigger automated communication based on specific user actions within the product. For example, a customer who hasn't utilized a key feature might receive an email offering guidance or highlighting its benefits.
c. Automated Milestone-Based Communication
Celebrate customer milestones (e.g., completing a training module) with automated emails that acknowledge their progress and potentially suggest next steps.
II. Data-Driven Insights And Feedback
a. Automated Customer Health Score Monitoring
Leverage automation to continuously monitor customer health scores, which can indicate potential churn. Trigger proactive outreach to at-risk customers based on dips in engagement or usage patterns.
b. Automated Sentiment Analysis
Utilize automation tools to analyze customer sentiment within support tickets, surveys, or social media mentions. This allows you to identify areas of frustration or satisfaction and tailor your engagement strategies accordingly.
c. Automated NPS (Net Promoter Score) Surveys
Schedule automated net promoter score surveys at strategic points in the customer journey. This provides valuable feedback on customer satisfaction and helps identify areas for improvement.
III. Personalized Recommendations and Upsells
a. Automated Feature Recommendation
Based on user activity, automate product recommendations that highlight relevant features or functionalities that can further enhance their experience and value extraction.
b. Automated Content Delivery
Utilize customer data and behavior to deliver personalized content through email, in-app notifications, or within the knowledge base. This ensures users receive information most relevant to their needs and current stage in the product journey.
c. Automated Upsell Opportunities
Leverage automation to identify customers who might benefit from an upgrade based on their usage patterns, feature adoption, or company size. Trigger targeted upsell campaigns with relevant messaging and pricing options.
IV. Streamlined Support And Self-Service
a. Automated Ticketing And Routing
Automate ticket routing based on predefined criteria like issue type, customer segment, or urgency. This ensures tickets reach the most qualified CSM for faster resolution.
b. Automated Knowledge Base Suggestions
Implement automated systems that suggest relevant knowledge base articles, FAQs, or troubleshooting guides based on the specific issue a customer is facing within the support portal.
c. Automated Chatbots
Utilize AI-powered chatbots to answer basic questions, troubleshoot common issues, and provide initial support 24/7. This reduces the burden on CSMs and offers customers immediate assistance.
3. Pre-Automation Retention
Churn reduction efforts often centered on personalized outreach, attempting to identify and address customer dissatisfaction before they left.

This reactive strategy left little room for proactive efforts to maximize customer value and prevent churn.
In the world before customer success automation, retaining customers in B2B SaaS was a constant battle.
Customer success teams relied on manual processes to identify at-risk customers and prevent churn, but these methods often felt like chasing after a moving target.
Here's a deeper look at the pre-automation approach to customer retention and its limitations:
I. Reactive Churn Management
Customer churn was primarily addressed reactively.
This meant waiting for customers to express dissatisfaction or show signs of inactivity before taking action. CSMs would scramble to salvage the relationship by offering discounts, addressing specific concerns, or attempting to understand the reasons for potential churn.
II. Limited Churn Detection
Identifying at-risk customers often relied on intuition or basic metrics like lack of login activity. Without sophisticated customer health scoring or usage analytics, it was challenging to proactively pinpoint customers who were likely to churn.
III. Manual "Save The Day" Efforts
When a customer expressed dissatisfaction, CSMs would engage in personalized communication to understand the issue and offer solutions. This reactive approach, while valuable, was time-consuming and didn't address the root cause of churn for a broader customer segment.
IV. Limited Upsell Opportunities
Identifying opportunities to upsell customers to a higher tier plan was based on manual analysis of usage data or conversations during check-in calls. This limited approach potentially left value on the table, as customers who could benefit from additional features might not be proactively offered upgrades.
The Challenges Of Manual Retention Strategies
I. Reactive Approach
Waiting for customers to express dissatisfaction meant valuable time had already been lost. Addressing churn after it began limited the effectiveness of retention efforts.
II. Inaccurate Churn Prediction
Relying solely on basic metrics or intuition for churn detection could lead to missed opportunities to intervene proactively with customers who were silently at risk of leaving.
III. Inconsistent "Save The Day" efforts
The effectiveness of customer retention depended heavily on the individual CSM and their ability to identify and address customer concerns. This could lead to inconsistencies in the level of effort and success rates across the customer base.
IV. Missed Upsell Potential
Without a systematic approach to identifying upsell opportunities, valuable revenue streams might be missed. Customers who could benefit from additional features might not be offered them, potentially hindering their overall success and satisfaction.
How Automation Can Improve Customer Engagement?
Here's a breakdown of what customer success teams can automate for improved customer retention:
I. Early Churn Detection And Intervention
a. Automated Customer Health Scoring
Utilize automated customer health scoring tools that analyze usage patterns, sentiment data, and support interactions. This allows for early identification of at-risk customers based on predetermined criteria.
b. Automated Churn Risk Alerts
Trigger automated alerts for CSMs when customer health scores dip or specific churn indicators are detected. This enables them to intervene proactively before issues escalate and potentially salvage the relationship.
c. Automated Pre-Cancellation Outreach
When a customer initiates the cancellation process, send automated emails prompting them to connect with their CSM. This personalized outreach can address concerns, offer solutions, and potentially prevent churn.
II. Personalized Communication And Support
a. Automated Win-Back Campaigns
For customers who have already churned, leverage automation to trigger targeted win-back campaigns based on their past usage and churn reason. Offer incentives or highlight new features that address their pain points.
b. Automated Milestone-Based Incentives
Celebrate customer milestones (e.g., exceeding usage targets) with automated rewards or discounts. This fosters a sense of value and encourages continued engagement.
c. Automated Sentiment Analysis-Driven Outreach
Utilize automation to analyze customer sentiment within support tickets, surveys, or social media mentions. Trigger proactive outreach to address frustration or dissatisfaction before it leads to churn.
III. Proactive Resource Delivery And Education
a. Automated Usage Triggered Resources
Trigger automated delivery of relevant knowledge base articles, tutorials, or in-app prompts based on specific user actions or lack of engagement with key features. This helps users overcome roadblocks and maximize their product value.
b. Automated Success Playbook Delivery
Develop automated workflows that deliver personalized success playbooks to different customer segments. These playbooks can outline recommended usage patterns, best practices, and key features to achieve specific goals, ultimately boosting customer success.
c. Automated Renewal Reminders and Communication
Send automated reminder emails before subscription renewals, highlighting the value proposition and offering support resources to ensure a smooth renewal process.
IV. Streamlined Feedback And Improvement
a. Automated Feedback Surveys
Schedule automated feedback surveys at strategic points throughout the customer journey. Analyze the feedback to identify areas for improvement and proactively address customer concerns before they lead to churn.
b. Automated NPS (Net Promoter Score) Surveys
Schedule automated NPS surveys to track customer satisfaction trends and identify at-risk customers. This allows for targeted interventions and continuous improvement efforts.
c. Automated A/B Testing for Onboarding and Engagement
Utilize automation to run A/B tests for different onboarding experiences or engagement strategies. Analyze the results and implement the most successful approaches to optimize customer retention.
Conclusion
While this manual approach fostered strong customer relationships, it lacked scalability.
As businesses grew and customer bases expanded, maintaining personalized touchpoints became increasingly challenging. This is where the magic of automation steps in.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Popular from Customer Success Management
Quality Content,
Straight To Your Inbox!
Subscribe for the latest blogs, podcasts, webinars, and events!

Write a Blog
If you have experience in CS and
a flair for writing, we’d love to
feature you.
Write to us on
hello@zapscale.com